Training and Sampling
MinT uses LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) for efficient fine-tuning. Instead of updating all model weights, LoRA trains small adapter matrices that are added to the frozen base model:
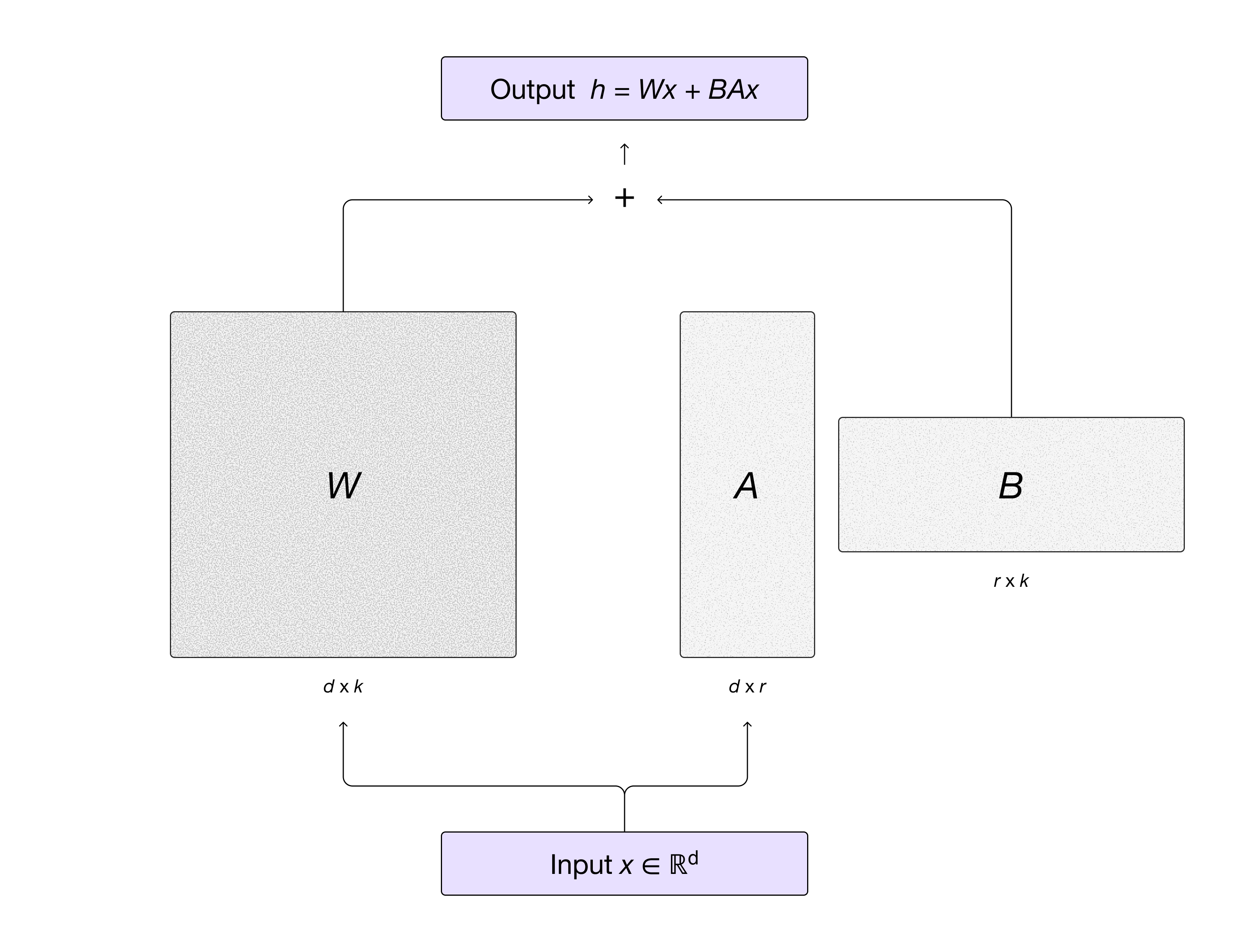
The output becomes h = Wx + BAx, where W is frozen and only the low-rank matrices A and B are trained. This dramatically reduces memory and compute requirements.
Creating a Training Client
import mint
service_client = mint.ServiceClient()
training_client = service_client.create_lora_training_client(
base_model="Qwen/Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507"
)Choose a base_model from the current Model Lineup.
Data Preparation
Convert your data to Datum objects containing model inputs and loss parameters:
- Tokenize prompts and completions separately
- Assign weights (0 for prompts, 1 for targets)
- Create shifted token sequences for next-token prediction
Training Loop
Gradient zeroing is handled automatically by the server. The correct pattern:
for _ in range(6):
fwdbwd_future = training_client.forward_backward(examples, "cross_entropy")
optim_future = training_client.optim_step(types.AdamParams(learning_rate=1e-4))Do NOT call zero_grad_async() - it does not exist in tinker 0.6.3 and is not needed.
Sampling
After training, create a sampling client to generate outputs:
sampling_client = training_client.save_weights_and_get_sampling_client(name='model')
result = sampling_client.sample(prompt=prompt, sampling_params=params, num_samples=8)Session Timeout
Sampling sessions have a 30-minute inactivity timeout. Sessions are refreshed automatically on each sampling request.
For long training runs (>25 minutes between samples), create a new sampling client each batch:
for batch in range(num_batches):
# Create fresh session each batch
sampling_client = training_client.save_weights_and_get_sampling_client()
# Complete sampling within 25 minutes
for step in range(max_steps):
result = await sampling_client.sample_async(...)
# Training update
await training_client.forward_backward_async(...)
await training_client.optim_step_async(...)See Limits and Quotas for all timeout values.
Logprobs
You can retrieve token probabilities:
include_prompt_logprobs=Truereturns token probabilitiestopk_prompt_logprobs=kreturns top-k alternatives per token position